937. Product of Array Except Self
Given an array in
of n integers, construct
an array out such that each element outi is equal to
the product of all elements of the array in except for ini.
Input. The first line contains an integer n (1 < n
≤ 106). The second line contains n integers, each with absolute value
at most 100.
Output. Print the array out.
It is guaranteed that the absolute value of each printed number does not exceed 2 * 109.
|
Sample
input 1 |
Sample
output 1 |
|
4 1 2 3 4 |
24 12 8 6 |
|
|
|
|
Sample
input 2 |
Sample
output 2 |
|
4 2 0 1 4 |
0 8 0 0 |
SOLUTION
arrays
Algorithm analysis
Let in be the input
array, and let us use 1-based indexing. Then the input values are stored in
in[1], in[2], …, in[n]. If we compute the product p of all
elements of the array in and then set outi = p / ini (where out is the resulting
array), this method fails when ini =
0.
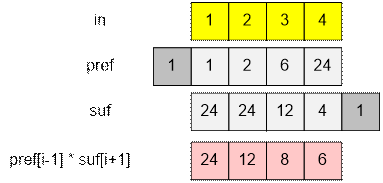
Let us consider a
different approach. We construct two arrays:
·
The prefix product array pref, where
pref[i] = in[1] * in[2] * … * in[i],
and we
define pref[0] = 1;
·
The suffix product array suf, where
suf[i] = in[i] * in[i + 1] * … * in[n],
and we
define suf[n + 1] = 1;

Then outi = pref[i – 1] * suf[i + 1].
Example
Algorithm implementation
Declare the arrays.
#define MAX 1000002
int in[MAX], pref[MAX], suf[MAX], res[MAX];
Read input data.
scanf("%d",&n);
for(i = 1; i <= n; i++)
scanf("%d",&in[i]);
// [1,2,3,4]
Build the array of prefix products.
pref[0] = 1;
for(i = 1; i <= n;
i++) // [1,2,6,24]
pref[i] = pref[i-1] * in[i];
Build the array of suffix products.
suf[n+1] = 1;
for(i = n; i >= 1; i--) // [24,24,12,4]
suf[i] = suf[i+1] * in[i];
Build the resulting array.
for(i = 1; i <= n; i++) // [24,12,8,6]
res[i] = pref[i-1] * suf[i+1];
Print the answer.
for(i = 1; i <= n; i++)
printf("%d
",res[i]);
printf("\n");